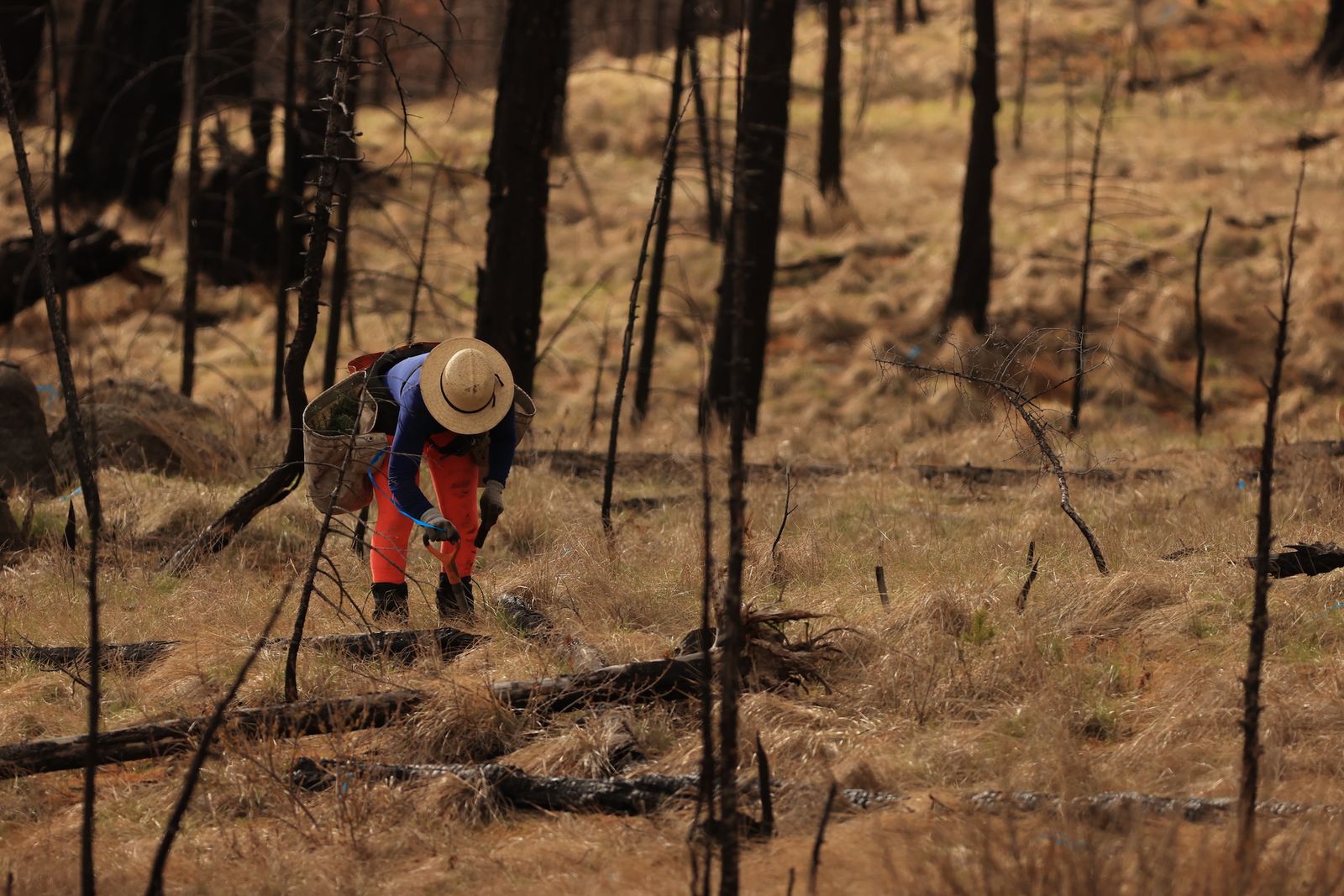

Rebuilding Oregon's Forests
American Forests’ Resilient Forests program restores forest health across the United States, Canada and Mexico, while focusing on helping forests adapt to stressors that climate change is making more severe and more frequent. These include extreme wildfire, deep droughts and outbreaks of pests and disease.
Species planted
-

Douglas Fir
The Douglas Fir is one of North America's most iconic conifers, reaching heights of over 250 feet and living for hundreds of years. Despite its common name, it’s not a...

Noble Fir
Native to the high-elevation forests of the Pacific Northwest, the Noble Fir is the tallest of the true firs, sometimes exceeding 200 feet in height. Its dense, symmetrical branches and...

Western Red Cedar
The Western Red Cedar is a massive, aromatic evergreen tree native to the coastal rainforests of the Pacific Northwest. Known for its reddish, rot-resistant wood, it has long been used...
1 / of 3Project Impact
Annual CO₂ 6.2 kgs/$Workdays 0.004The reforestation in Oregon has brought about a multitude of environmental and social benefits. The first is habitat restoration. By restoring forest cover the project helps preserve habitats for both threatened and endangered species such as Deer, Elk, Cougar, Bear, Trout and Spotted Owl.
As well as habitat protection the project has great benefits for mitigating climate change through the carbon sequestered. The trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating climate change. For every tree planted an estimated 0.77 tonnes of CO2 is sequestered across its lifetime.
Not only great for the environment the project has brought about a significant level of economic uplift and opportunities for community members. For every 10,000 trees planted, 40 work days are created for community members. Helping ensure that the project is not only great for the environment but also great for people.
Project location
Silver Falls State Park, Oregon, United States
1 / of 3Why plant in United States
Project Details
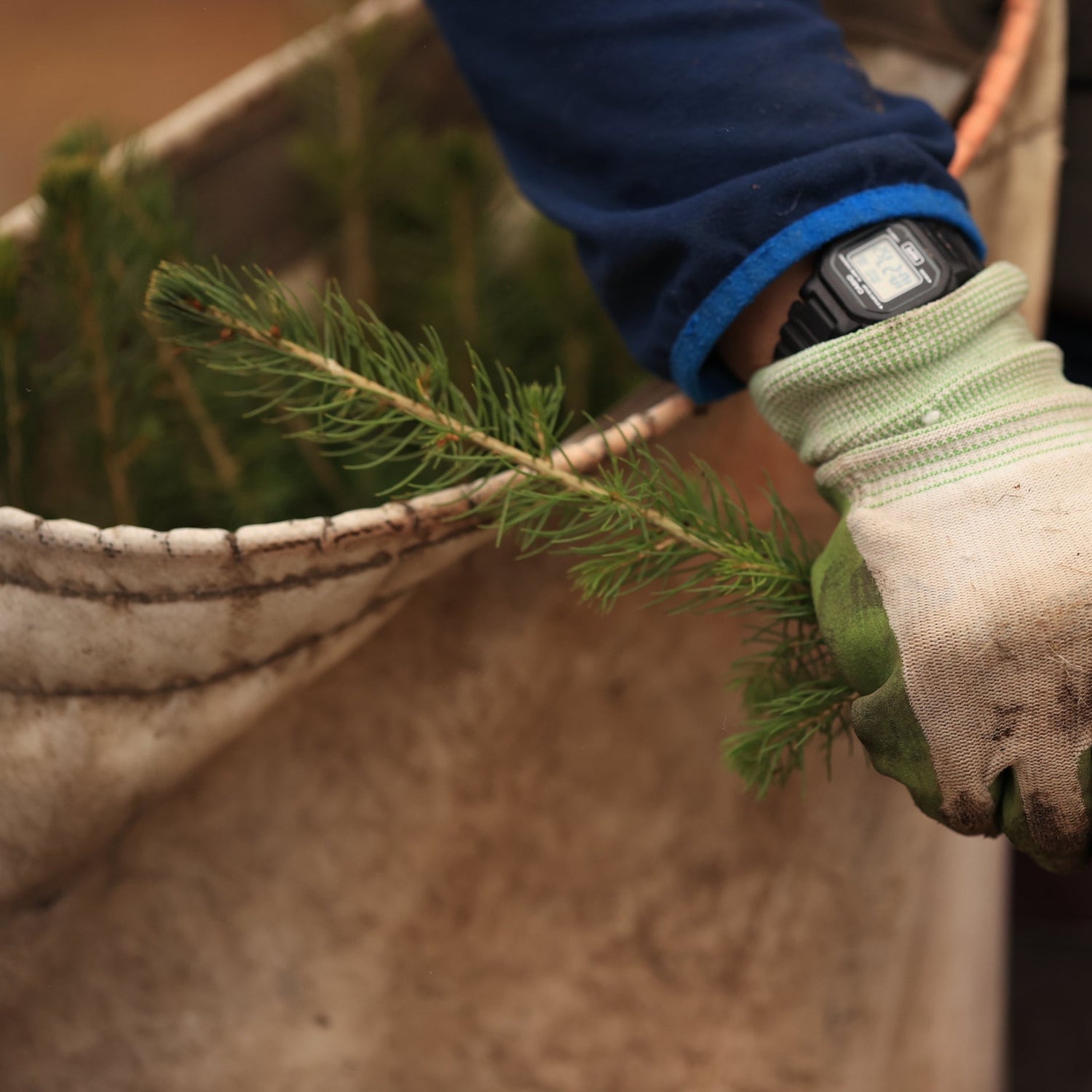

What is Reforestation?
Reforestation is the process of restoring trees in areas that have experienced deforestation or forest degradation, which can occur due to various natural and human-induced factors such as urbanisation, agriculture, infrastructure development, forest fires, mining and more. The process involves planting trees or allowing natural regeneration to occur, aiming to rebuild forest ecosystems and restore their ecological functions.
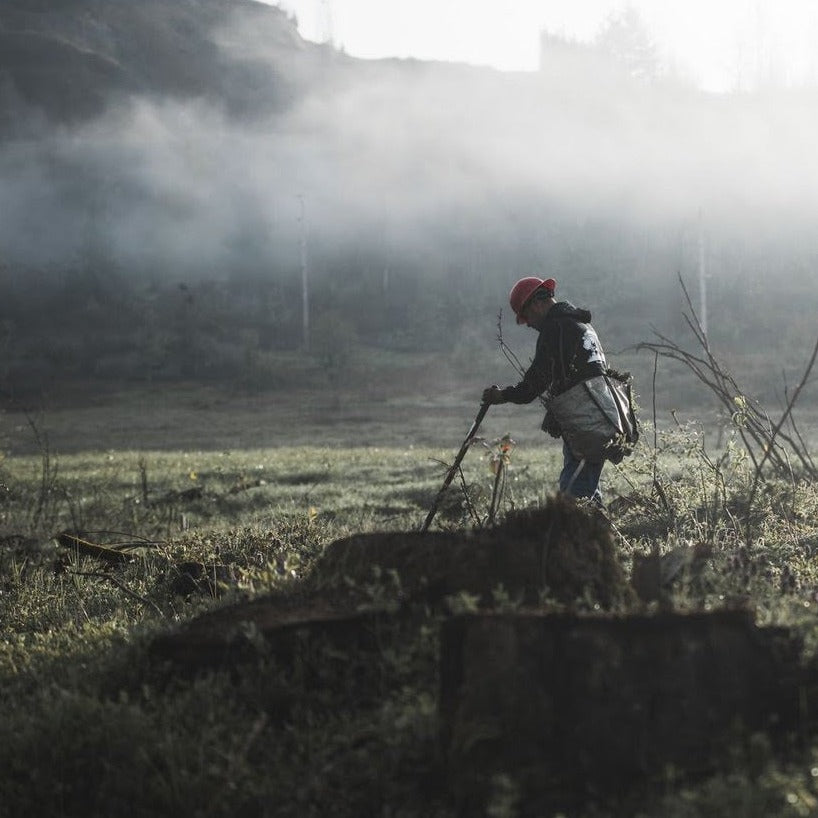

The Importance of Reforestation in Oregon Following Forest Fires
Wildfires in Oregon have become increasingly severe in recent years, devastating vast tracts of forested land. These fires not only destroy trees but also disrupt ecosystems, displace wildlife, and contribute to air and water pollution. The damage extends beyond the immediate area of the fire, affecting climate regulation, water cycles, and soil health. The loss of forests reduces the natural capacity to sequester carbon dioxide, exacerbating climate change. The smoke and particulate matter from wildfires also pose significant health risks to nearby communities, impacting air quality and public health.
The need for reforestation in Oregon is critical in the wake of these wildfires. Replanting trees helps to restore the devastated landscapes, supporting the return of wildlife and the recovery of ecosystems. It also plays a key role in stabilizing the soil, preventing erosion and reducing the risk of landslides. Furthermore, reforestation efforts help to rebuild the natural carbon sinks, mitigating the effects of climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Reforestation in Oregon also provides economic and social benefits. Restored forests can support the local timber industry, create jobs, and boost tourism and recreation. Engaging communities in reforestation projects fosters a sense of stewardship and connection to the environment. Ultimately, reforestation is essential for restoring the health and resilience of Oregon’s forests, ensuring they continue to provide ecological, economic, and social benefits for generations to come.
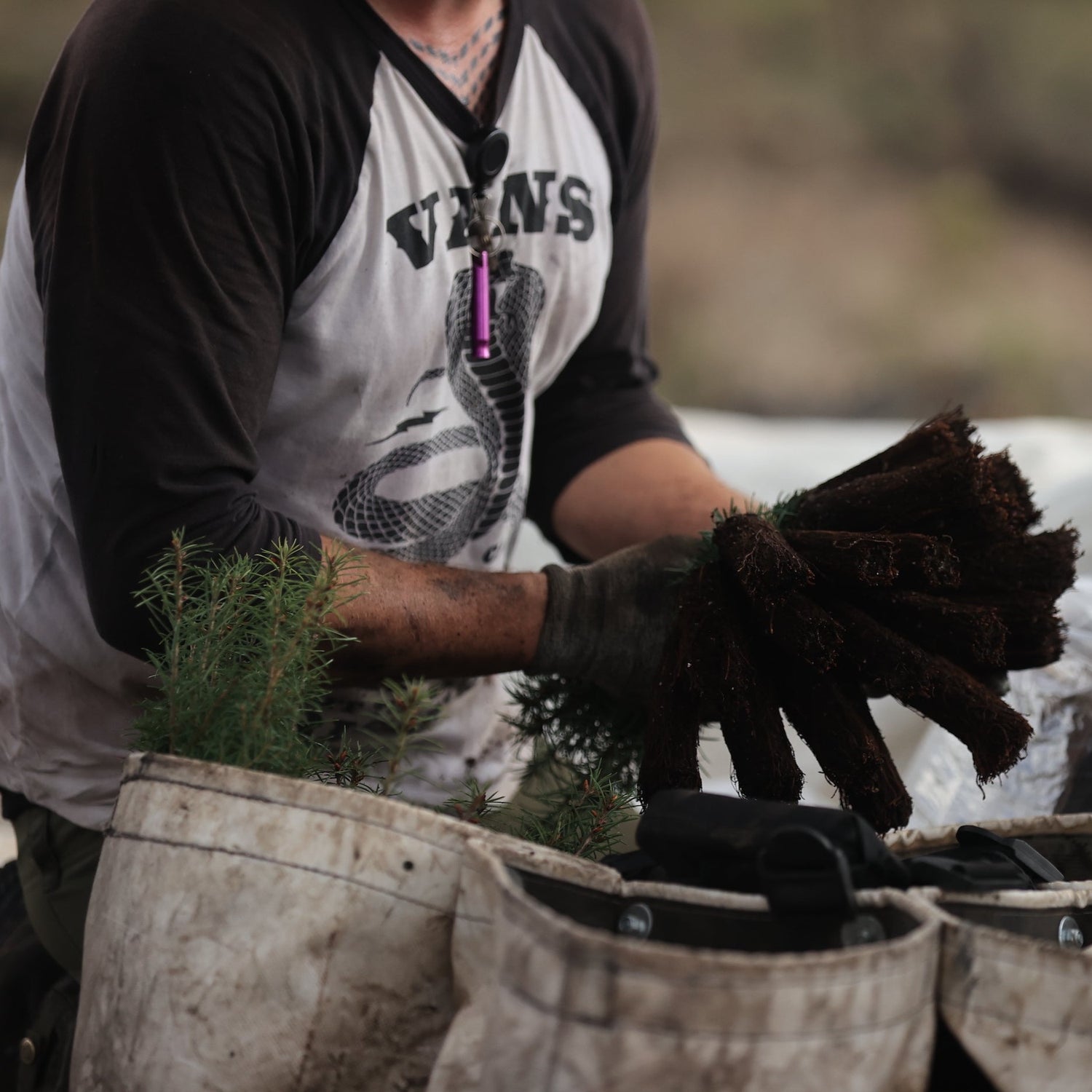

The Process of Reforestation
Reforestation involves six key steps to ensure the successful establishment of new trees:
- Planning: Before planting begins, the area slated for reforestation is carefully assessed by forestry professionals. This assessment includes identifying indigenous tree species and evaluating soil conditions to determine the most suitable species and planting density.
- Seeds: High-quality seeds from native tree species are collected and processed, either from the wild or through nurseries. Seeds are carefully selected based on their origin and characteristics to ensure genetic diversity and resilience.
- Nursery: Seeds are germinated and grown into seedlings in nurseries under controlled conditions. Seedlings are nurtured until they reach the optimal size for planting, typically a few months old and several inches tall.
- Site Preparation: In some cases, site preparation may be necessary to create optimal growing conditions for seedlings. This may involve techniques such as trenching or mounding to improve soil structure and drainage.
- Planting: Seedlings are transported to the reforestation site and planted by professional crews. Planting methods vary but typically involve digging holes and carefully placing seedlings, ensuring proper spacing and root integrity.
- Monitoring & Verification: After planting, ongoing monitoring is conducted to assess the growth and survival of newly planted trees. This includes tracking environmental conditions and using advanced site technology to ensure project objectives are met.
UN Sustainable Development Goals contributed to
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 interconnected global objectives aimed at addressing pressing social, economic, and environmental challenges by 2030. They serve as a blueprint for collective action, guiding governments, businesses, and communities worldwide towards a more sustainable and equitable future.
This project contributes to the following goals
Verification
To ensure the success and accountability of reforestation efforts, advanced site technology is utilised for monitoring and verification. Technologies such as dendrometers, soil sensors, tree vision systems, and weather stations enable precise data collection and analysis, ensuring the effectiveness of restoration initiatives. Read more about American Forests here.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.
Customize your planting
Select your planting project
Africa
Americas
Asia
Claim your reward!
Your reward!
Your friend has gifted you a rewardHere is your coupon codeEnter your email address to receive the reward.











